TREATMENT
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS IN INFERTILITY ACCORDING TO THE TREATMENT
TREATABLE DISEASES
Varicocele
Obstructions (Congenital or acquired)
Infection
Ejaculatory dysfunction
Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism
Immunologic problems
Hyperprolactinemia
POTENTIALLY TREATABLE DISEASES
Idiopathic
Cryptoorchidism (undecended testes: Retantio testes)
Vasal agenesis
Gonadotoxins (drugs – radiation)
NON-TREATABLE DISEASES
Bilateral anorchidia
Germinal cell aplasia
Primary testicular failure
Chromosome abnormalities
Immotile cilia syndrome
(pregnancy may be achieved with ICSI in some diseases within this group!)
- Empirical Medical Treatment:
Here, drug therapy is applied by trial and error without cause oriented.
Clomiphene Citrate: It presents an antiestrogenic effect by binding estrogen receptors in hypothalamus and hypophysis. Thus, estrogen decreases and FSH, LH, GnRH increase. Increase of these increases testosterone. It may be applied in low sperm count. Dose is 12.5 – 50 mg/day continuously or discontinuation for 5 days every month.
Tamoxifen: It is anti-estrogenic. It is applied as 10 to 15 mg twice a day for 3 to 6 months.
Kallikreins: It provides stimulation on spermatogenesis, induction on sperm motility and sperm forwarding along female reproduction system. Kallikrein is a pancreatic enzyme and releases quinine. It increases sperm motility, testicular blood flow and stimulates sertoli cells. Pregnancy is present by 38%.
Antioxidant Therapy: It has been found in 40% of infertile men that free oxygen radicals have increased. These cause reaction on sperm membrane. Vitamin E and Glutation are given.
- Surgical Treatment:
Varicocele: Varicose spermatic vein ligation is performed retroperitoneally, inguinally and subinguinally. This procedure is also applied with percutaneous embolization and laparoscopy. The purpose is to eliminate the retrograde blood flow. Pregnancy ratio in average: 35%.
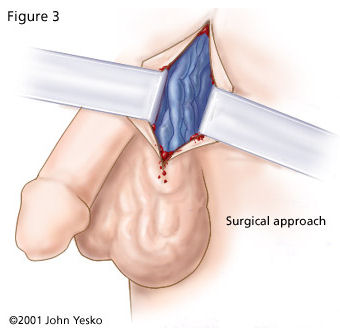
Vasovasostomy: Vasovasostomy is applied for infection, trauma, deformity cases beyond those returned from vasectomy. Two layer anastomosis is performed here. Sperm is detected in ejaculate after vasovasostomy with a rate of 95%.
Endoscopic Resection of Ejaculatory Duct: Obstruction of Ejaculatory Duct is seen in 5% of azospermic patients. It should be considered for a patient who have ejaculate below 2 ml and fructose. Expected pregnancy rate is 20 to 30%. Complication rate is 20%.
Electro-ejaculation: Emission and ejaculation failure occurs due to pelvic sympathetic nerve injury in spinal cord injury. Therefore, reflex ejaculation is provided with rectal electro-probe. These patients may have retrograde ejaculation.
Sperm Aspiration: It is indicated for those without any duct system and deformed sperm motility. Aspirated sperms by using microsurgery are used for IVF.
- Assisted Reproductive Techniques:
Developments in molecular biology, immunology, genetic sciences allow women who have been considered to get pregnant impossible until 10-15 years ago to get pregnant easily today.
IUI (Intrauterine Insemination): Artificial fertilization: Inoculation:
Sperms taken from men is irrigated and mixed with some specific strengthening agents and placed into the uterus. (Cervix is by-passed) primary indication is cervical factors within women. Furthermore, it may be applied for immunologic infertility or unexplained infertility which are male factors. At least 5 to 40 million motile sperms are required in ejaculate. Pregnancy rates varies between 8% and 16%.
* Donor insemination: It is prohibited in Turkey!!! It includes inoculation or invitro fertilization techniques performed by using sperm of a men who is not husband of the woman taken from a sperm bank.
IVF (Invitro Fertilization = or IVF-ET (Invitro Fertilization – embryo transfer)
It is performed as a remedy for women originated or unexplained infertilities. In this application, mature follicles are created in ovaries by ovulation induction (drugs providing ovulation) in woman. Then, these mature follicles are removed from the body of the woman with different methods and combined with the sperms obtained from the man via masturbation in laboratory environment. Semen should include 100,000 to 200,000 sperms at least. After a period, some sperms fertilize oocytes (ovum cell). If fertilization occurs, some of the embryos are put into the uterus. Multiple pregnancy possibility is high.
GIFT (Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer): The ovum is removed laparoscopically and combined with the sperm and injected into the fallopian tube via a laparoscope. Invivo fertilization formation is provided. The disadvantage is that it is unclear whether fertilization is present. Lately, some methods such as PROST (pronuclear stage tubal transfer), ZIFT (zygote intrafallopian transfer), TET (tubal embryo transfer) veTEST (tubal embryo stage transfer) which combine IVF principles and GIFT principles have been suggested. The purpose here is in-vitro fertilization and injection into the fallopian tube within early stages. The main rule is to have one intact fallopian tube at least.
MICRO-MANIPULATION: (TUBE BABY)
If fertilization can not be created with standard techniques or there are less or unqualified sperms, one of these techniques is used.
The membrane around ovum, Zona pellucida is one of the most important obstacles for sperm penetration. All micro-manipulation techniques base on by-passing this obstacle.
- Zonal drilling: Zona is tried to be drilled by using an acidic solution.
- PZD: Partial zona dissection : Zona is cut mechanically.
- SZI: Subzonal sperm injection:
- ICSI: Intracytoplasmic sperm microinjection: Sperm microinjection into ooplasm:
Even 1 sperm is enough here. A single sperm is pushed into the ovum by microscopic techniques. Pregnancy rate per cycle is about 30%.
The ethical is to apply this technique as ultimate remedy for the cases whom achievement could not be provided after application of all standard techniques. It is very expensive and inconvenient technique morally. This procedure should be applied in competent centers with a team approach (gynecologist – urologist- embryologist etc.).
TESE / MICRO TESA / MESA / PESA:
In all these methods, alive sperm is searched by performing a surgical intervention into the testicles or epididymis to azospermic or severely oligospermic men under local or general anesthesia before test-tube baby procedure. If alive sperm is obtained during the operation, it is either used for his wife or sperms are frozen and stored to be used further. (sperm freezing)





